Metal Injection Molding vs Forging
Metal injection molding vs Forging are two total different metalworking methods. These two technologies result in different properties for final metal parts. Metal Injection molding (MIM) technology normally produces high tolerance metal parts within complex geometries. Forging technology produces ultimate metallurgical performance consistently, specific in superior fatigue and strength properties.
Metal Injection Molding
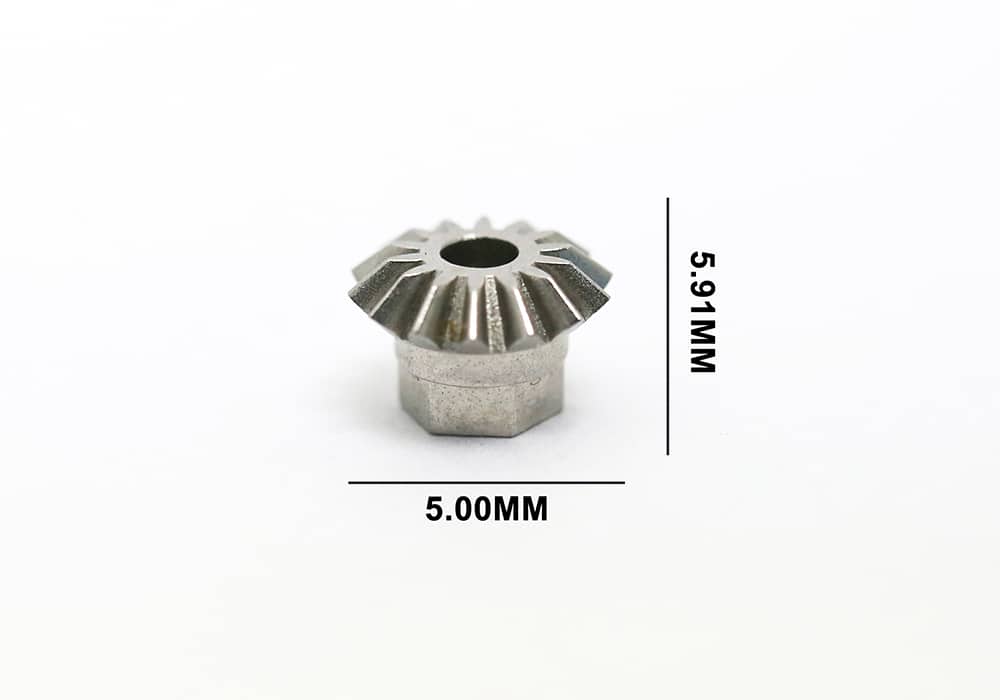
Metal Injection molding is an advanced metalworking technology, it can produce high precise metal parts with complex structure and excellent properties. MIM technology combines the normal forming process in injection molding and the sintering process in powder metallurgy. The common MIM process including 4 steps.
- Mix super-fine metal powders with binder materials, then extrude and chop the mixture into tiny pellets – Feedstock
- Insert MIM feedstock into mold cavities of common injection molding machine, then form required structure with high pressure – Green Part
- Remove the binder materials from molded parts, the debinding method including solvent, catalytic, heating – Brown Part
- Sinter debinded parts in different temperatures, burn the remaining binders at first, then densify metal powders with less porosity.
Metal injection molding has less limitation in component design, it can create asymmetric and irregular feature sin one single part. While all these features are difficult or impossible to manufacture by traditional metalworking methods, such as CNC machining, die casting, investment casting. MIM technology has its unique geometry’s capability, this make it wide application in various industries, such as medical, dental, electronic, automotive, industrial.

Metal Forging
Metal forging is a traditional metal manufacturing process, metals are shaped and formed into customized structure by compressive forces, from hammering, pressing, or rolling. Forging is the pivotal metalworking process in the metal manufacturing industry, especially vital in the iron and steel industries. Depends on the temperature of working metals, forging is classified into cold forging, warm forging, and hot forging.
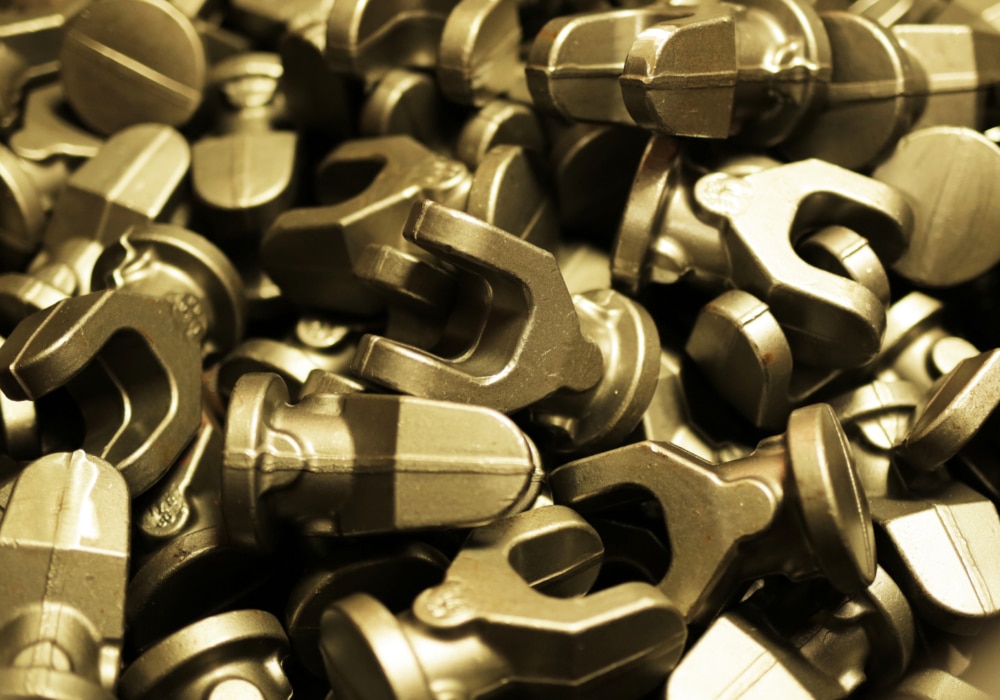

Metal Forging Process
Once choose metal forging technology for critical metal component production, it is challenging to make the right choice. As each forging technique has varying pros and cons. However, metal forging method has unique advantage unavailable with any other choice. Especially in requirement of maximum strength, custom sizes, and critical performance specifications. The most common metal forging methods including: closed die forging, open die forging, cold forging, roll forging.
Closed die forging
Closed die forging applies the die to cover the workpiece entirely or partially. In this process, the heated meta is placed in the bottom die, then shaped by the top die into the required form. The raw materials should have the nearing shape or size of the final forged parts. Closed die forging can manufacture different size from 200 grams to 30,000 kilograms.
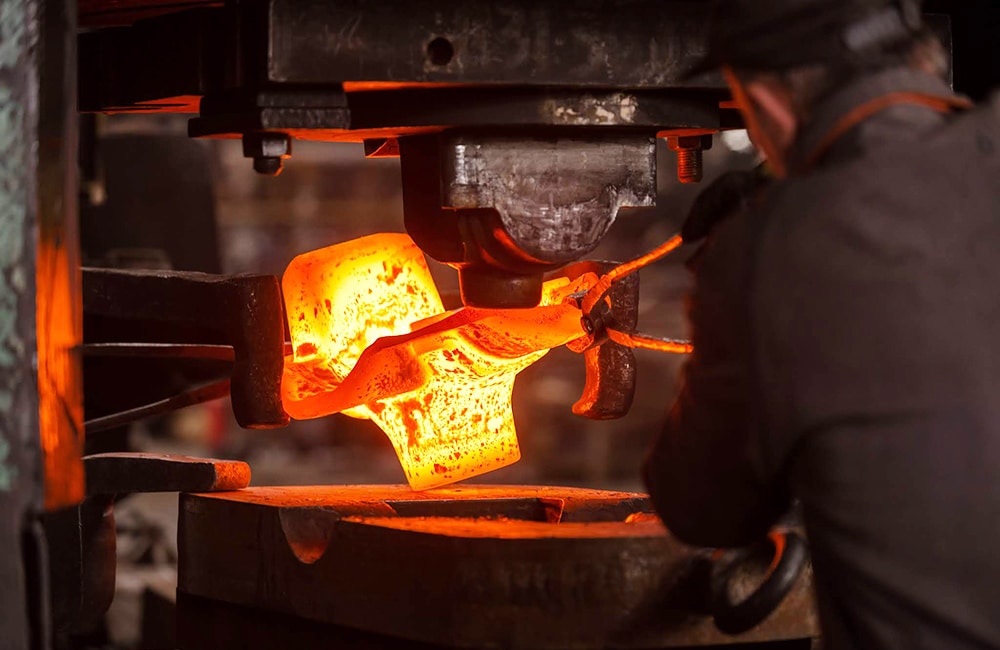

Open die forging
In open die forging, the metal isn’t confined or restrained in the dies completely. Heated metal parts are formed between a top die with a ram, or a bottom dies with a bolster, anvil, hammer. The typical forging temperature is between 260 ℃ to 1320 ℃, the different appropriate temperatures are applied with different metal materials. Normally, the open die forging is suitable for large and simple shape parts, such as bars, rings, and hollows.
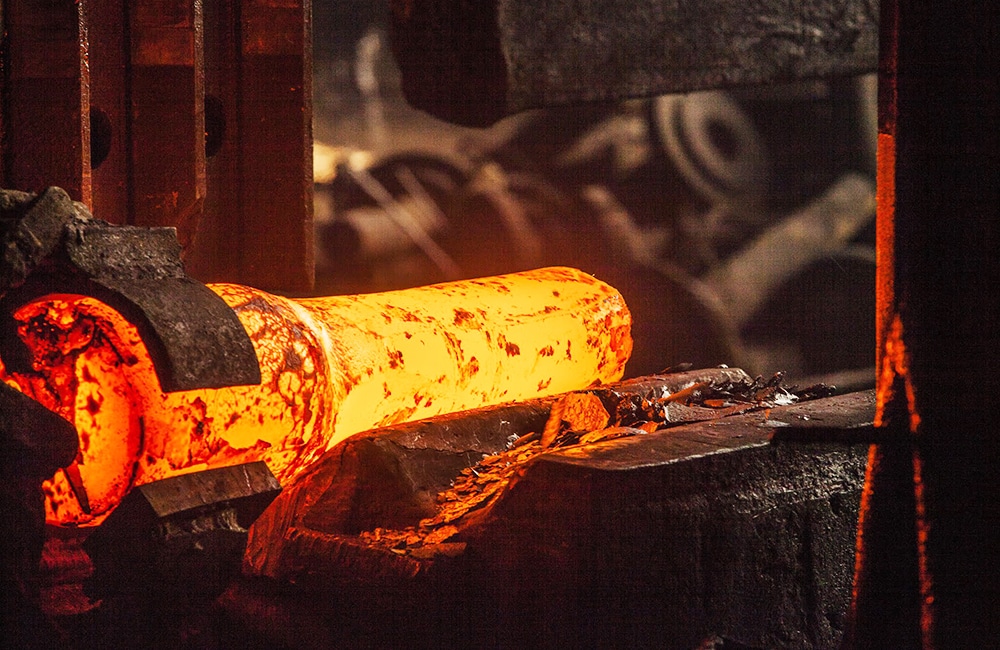

Cold forging
Cold forging refers to forging at the temperature from room temperature to several hundred degrees. This process encompasses numerous forging techniques, including: bending, extruding, cold drawing, coining and cold heading. Normally, cold forging requires more powerful equipment to manufacture many metal, like high carbon steel. It has more advantages than hot forging in dimension control, production uniformity, surface finish and contamination. Cold forging is frequently in automotive steering and suspension parts, anti lock-braking system.
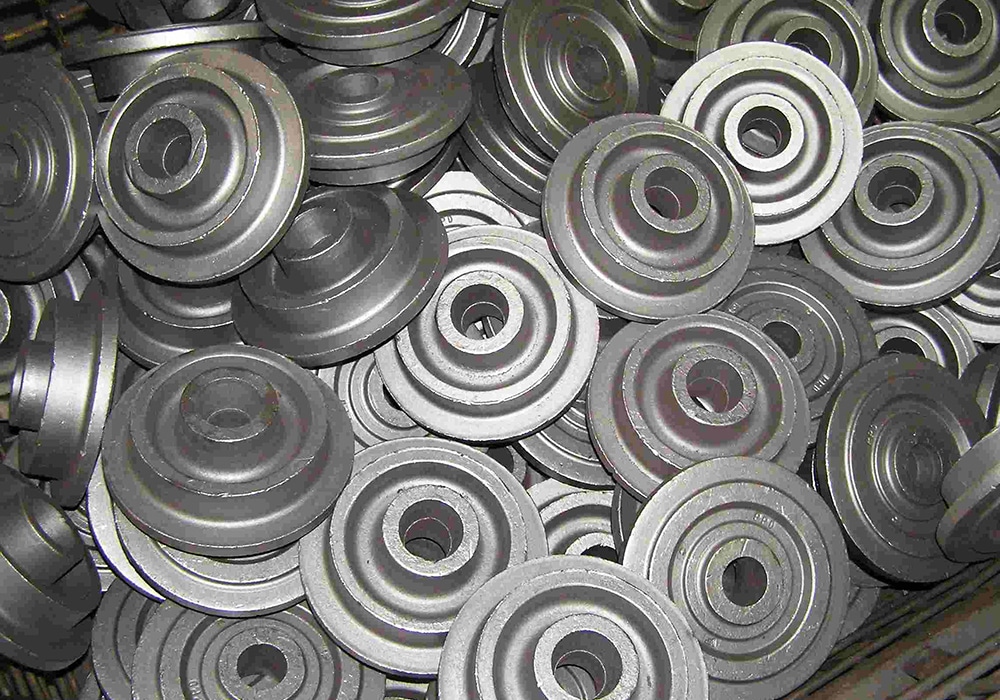

Roll forging
Rolling forging is also called roll forming, it applies opposing rolls to form metal parts. In this process, two cylindrical or semi-cylindrical rolls are applied to deform bar stock, in order to reduce the thickness or increase the length. There is no doubt that roll forging have superior mechanical properties than other metalworking process. Roll forging is suitable for products in automotive industry, or knives and hand tools in kitchenware industry.
Metal Forging Materials
The different metal types determine the final forging process. All metals have different characteristics and properties, which are in relation to weight, tensile strength and deformation capabilities. The common metal type for forging including:
- Carbon steel, stainless steel
- Hard tool steel
- Aluminum
- Titanium
- Brass and copper
- High-temperature alloy (cobalt, nickel, molybdenum)
Metal Forging Benefits
In reason of many positive features of forging, it has been a central metal forming technology for many years. Forging can supply strong, lasting and reliable metal parts with optimum performance.
Directional Strength
The controlled deformation in forging process result in metallurgical soundness and exceptional mechanical properties. Both pre-heating and forging process will create the proper grain flow, directional properties of strength and ductility.
Resistance to Fatigue
Other metalworking methods will result in fatigue and corrosion sensitivity, in reason of the exposure of grain flow lines on the surface. However, the forging process maintains the grain flow following with the contour and shape. In order to increase fatigue and corrosion resistance.
Design Flexibility
Engineers are able to create forging parts with great strength, they understand the affection of the grain flow, and make design to resist fatigue and failure. Forging allows designers to select the perfect materials and heat treatments for each component. In order to achieve required mechanical strength, resilience, and impact resistance.
Excellent Strength
The primary benefit of forging is the excellent strength of completed products. That is because metal can retain its grain structure and alignment in forging process. Pre-processing and pre-working will remove any contaminant concerns, then the metal will solidify flawlessly during the recrystallization process.
Metal Forging Limitations
Metal forging is inability to produce metal parts with complex shapes and structures. Although highly specialized tooling can enable specific products, forged configurations are limited to less complex shapes.
MIM vs Forging Comparison
Materials Options
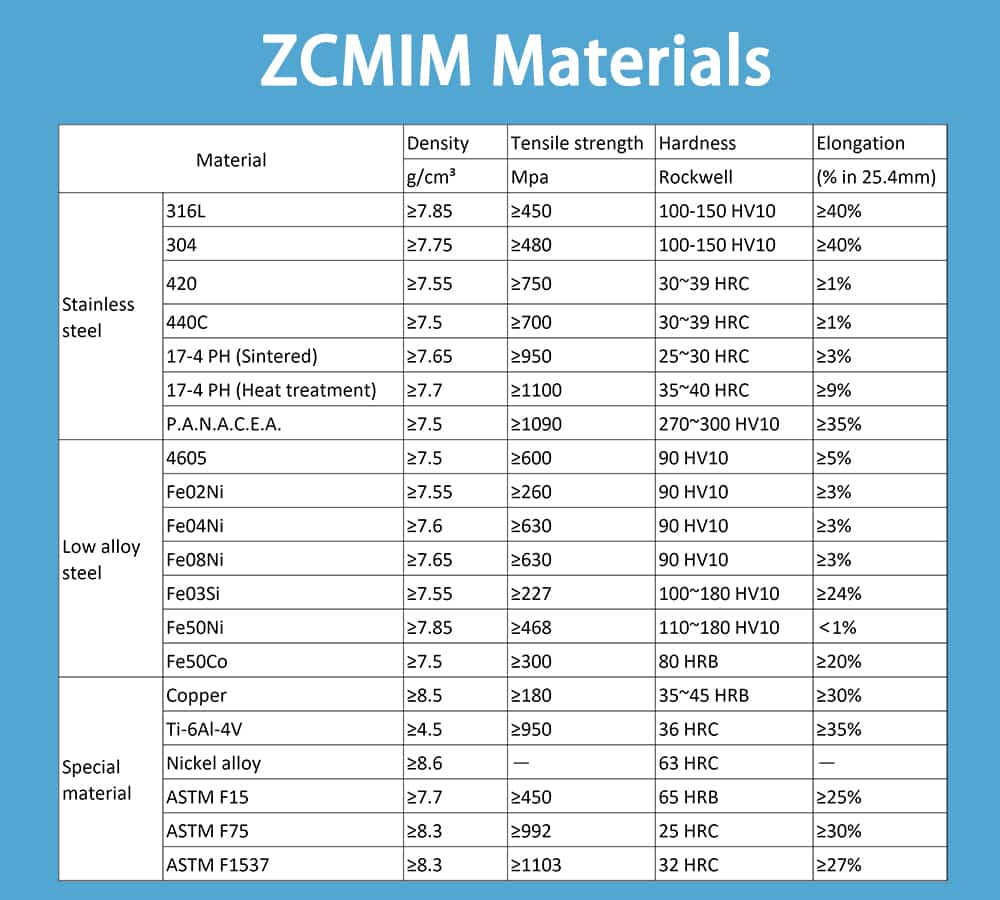
Both metal injection molding vs metal forging can produce durable metal parts. However, metal forging provide wider metal options, near any metal can be manufactured by forging process. MIM is more suitable for alloys with high melting temperature, aluminum or zinc alloys are not feasible in MIM technology.
Product Size
Metal injection molding is a cost-effective metalworking for small size parts with high precision. Its maximum size is 250 grams weight. However, metal forging is able to manufacture different size from hundreds of grams to thirty thousand kilograms.
Dimensional Tolerance
MIM technology is able to achieve high tolerance of ±0.01 mm, while the normal tolerance of drop-forging is ±0.5 mm. In forging process, it is difficult to achieve high tolerance, we normally make sure tolerances have no effect on assembling.
Final Properties
Forging can create metal parts with excellent properties, it provides the highest strength and resistance to fatigue and corrosion. Metal injection molding technology is able to produce MIM parts with according properties on MPIF Standard 35. However, it is obvious that MIM technology only can reach almost 90% of strength comparing to forging process. Forging process can achieve better strength than CNC machining.
When To Use MIM vs Forging
MIM vs Forging have different capability in metal manufacturing. Metal injection molding is perfect for small metal parts with high-volume production, while metal forging is suitable for simple metal parts with excellent strength. In addition, from the forging experience, we can apply various heating treatments (annealing, tempering) to increase required strength of MIM parts.

Conclusion
ZCMIM has focused on metal injection molding technology for decades, our excellent experience can ensure the production of high quality MIM parts. Furthermore, additional heating treatment can increase unique property significantly, which is almost can reach to the level of forging parts.