MIM 4340
Introduction
4340 Steel is a nickel-chromium-molybdenum steel with high hardnability and tensile. It is an ultra-high strength steel, it is classified to medium-carbon low alloy steel. 4340 steel has high strength, ductility, toughness, creep & fatigue resistance. Its hardness has range from 200 to 400 HV1 with different heat treatment.
Hardened and tempered 4340 can be surface hardened again by flame or nitriding induction. Normally, 4340 is applied in sectors with higher tensile/yield strength than 4140. As the highest quality steel, 4340 has excellent transverse ductility and toughness at high strength levels. It also has good shock and impact resistance, wear and abrasion resistance in the hardened condition.
Common Chemical Composition
| MIM 4340 | Iron | Nickel | Chromium | Molybdenum | Carbon | Silicon | Manganese |
| Percent by Weight | Bal. | 1.50-2.50 | 0.75-1.25 | 0.20-0.30 | 0.30-0.60 | ≤1.00 | ≤1.00 |
Mechanical Properties (Sintered)
| Material | Density | Tensile Strength | Yield Strength(0.2%) | Hardness | Elongation(% in 25.4mm) |
| MIM 4340 | ≥7.50g/cm³ | ≥750Mpa | ≥500Mpa | ≥200HV1 | ≥5% |
Mechanical Properties (Quenched + Tempered)
| Material | Density | Tensile Strength | Yield Strength(0.2%) | Hardness | Elongation(% in 25.4mm) |
| MIM 4340 | ≥7.50g/cm³ | ≥900Mpa | ≥750Mpa | ≥400HV1 | ≥2% |
Common Applications
Due to the primary toughness, steel 4340 is suitable for heavy machinery, specially for transmission, like heavy duty shafts, gears, and axles. Other industry, including: military aircraft, landing gear in commercial aircraft industry, rocket motor cases, pressure vessels, fasteners, ordnance hardware.
Components with high strength and toughness:
- Automotive parts – shafting, fasteners, hydraulic systems, heavy duty shaft
- Mechanical engineering parts – gears, axles, coupling, pins, spindles
4340 Steel Equivalent Grades
| USA | EU | Germany | Japan | France | England | Italy | China | Russia | Inter |
| 4340 | 34CrNiMo6 | 1.6582 | SNCM447 | 35NCD6 | 817M40 | 35CrNiMo6 | 40CrNiMo | 40KHN2MA | 36CrNiMo6 |
4340 Alloy Powder
In ZCMIM, we are able to develop different raw materials mixes and processing routes to satisfy different specifications. For 4340 alloy powder, we can provide three types:
- 90%-16µm gas atomized prealloy powder
- 90%-22µm gas atomized prealloy powder
- master alloy powder (90%-22µm) + carbonyl iron powder(CIP)
Different 4340 powder will result in different properties in different sintering temperatures, like densificaiton, tensile strength, surface hardness.
4340 Sintering
Carbon Control
The carbon content in final sintered 4340 parts are within the target specificaiton of 0.35-0.5%. The observed value of 90%-22µm, 90%-16µm and MA+CIP are 0.37%, 0.38%, 0.37 respectively at sintering temperature of 1100℃. In addition, similar data are achieved in other sintering temperatures.
Sintering Parameter
4340 is normally sintered in nitrogen atmosphere. The 4340 sintering temperature is in the range of 1000-1300℃, with holing time of 2-4 hours. Then slow cooling under the nitrogen atmosphere.
Sintering Density
From the following density graph, all interconnected porosity is removed at different temperature: MA+CIP and 90%-16 µm powders at 1100℃, while 90%-22 µm powder at 1200℃. All densities increase between 1200 to 1300℃, and achieve maximum value at 1300℃.
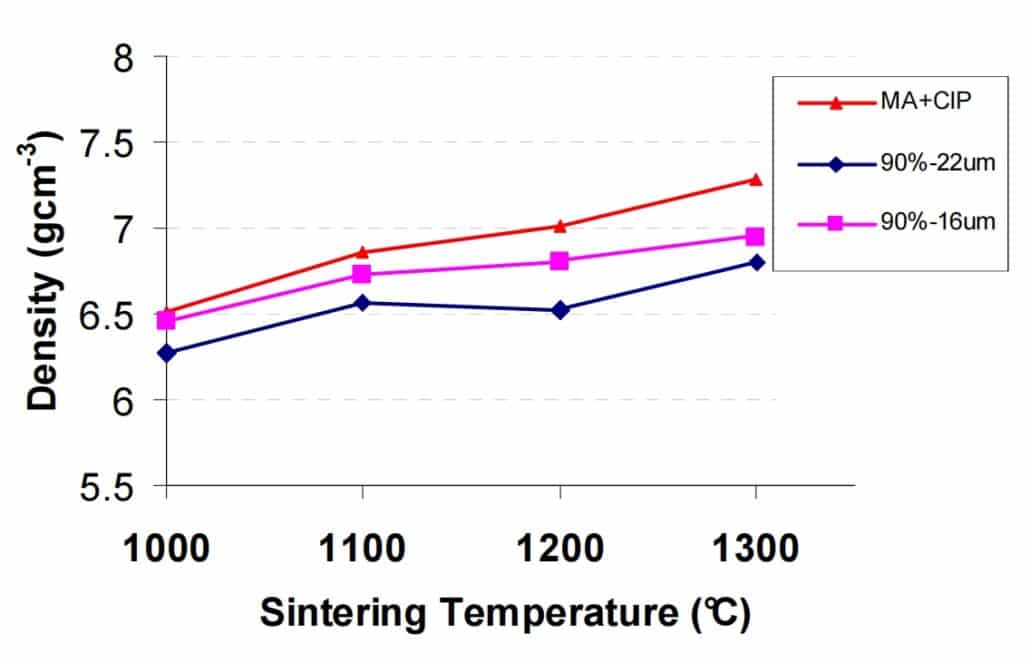
4340 Density in Different Sintering Temperature
Micro-structure after Sintering
From the following micro-graph of 4340 in different temperatures. At 1000℃ sintering, there are large MA particles in the bainite matrix without full diffusion. While 4340 is fully bainitic at 1100℃.
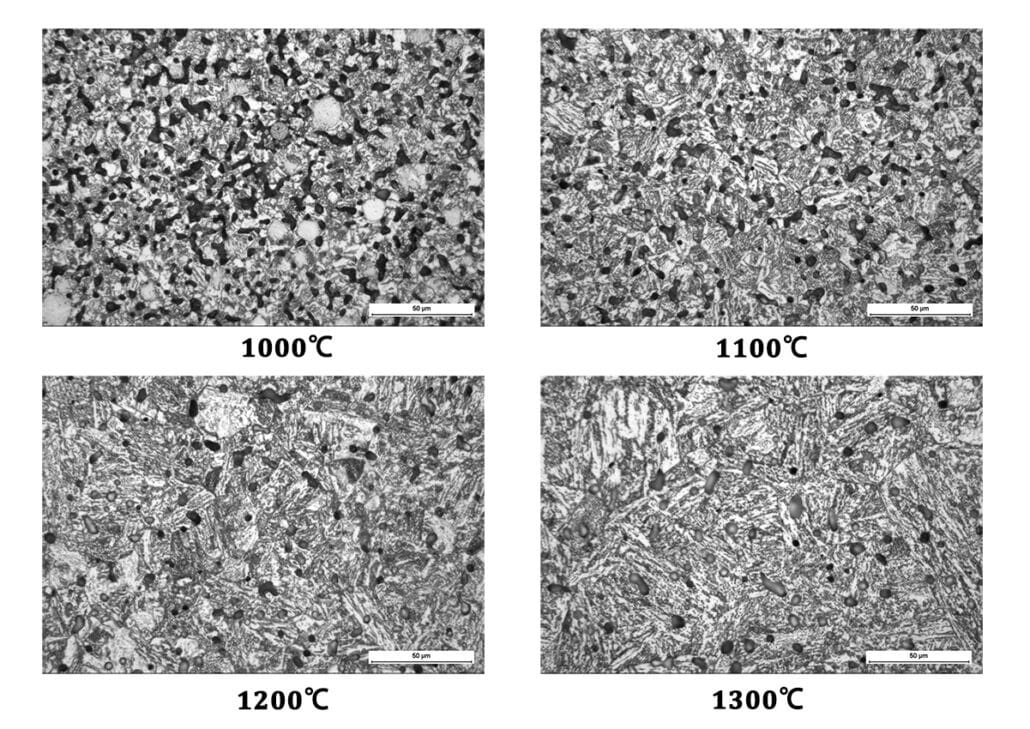
4340 Micro-structure in Different Sintering Temperature
Sintered Hardness
Hardness value of 4340 after 250℃ tempering is shown in following picture, the MA+CIP powder record the highest hardness at 1200℃ sintering temperature.
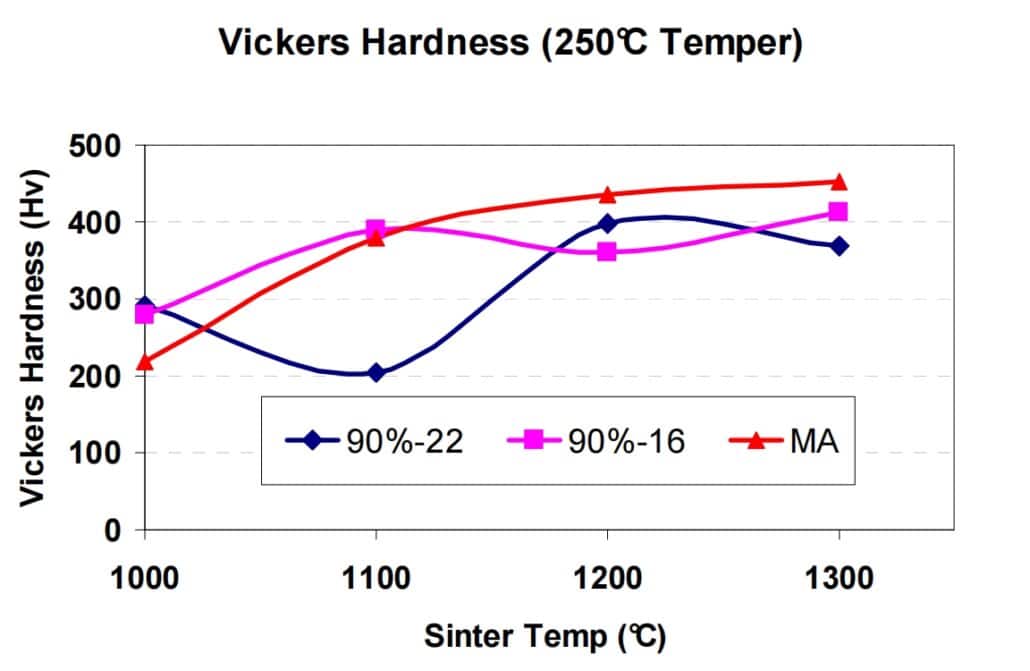
4340 Hardness in Different Sintering Temperature
Heat Treatment of MIM 4340
Annealing
Heat to 800-850℃, hold until the temperature is uniform in the section. Then cool down to 315 ℃ in the furnace at rate less than 10℃ per hour. Finally, air cool to room temperature.
Flame or Induction Hardening
Hardened and tempered 4340 is able to harden by the flame or induction hardening methods, in order to achieve surface hardness of 50 HRC. According to required hardness, work-piece size/sharp, quenching arrangements. Heat as quickly as possible to the austenitic temperature range of 830-860℃, then quench immediately in oil or water. After quenching to hand warm, tempering between 150-200℃ to remove quenching stresses. This has little effect on hardness.
Normal Hardening
Heat to 830-860℃, hold until the temperature is uniform in the section. Then soak 10-15 minutes per 25mm section, and quench in oil, water, or polymer. Finally, tempering immediately while still hand warm.
Nitriding
Hardened and tempered 4340 can also be nitrided successfully, in order to achieve surface hardness of 60HRC. The Nitriding is processed at temperature of 490-530℃, then slow cooling (no quench) to eliminate the distortion problems. The nitriding temperature is generally below the original tempering temperature, there is no effect on the tensile strength.
In addition, the nickel is insert to the nitrogen action, and resists the nitrogen diffusion into steel. This results in longer nitriding cycle times or lower surface hardness in nickel steel like 4340.
Stress Relieving
Heat to 600-650℃, hold until the temperature is uniform in the section. Then soak for 1 hour per 25 mm section, cool down in still air.
Tempering
Re-heating to 450-660℃, hold until the temperature is uniform in the section. Then cool in still air after soaking for 1 hour per 25 mm section. Notice to avoid tempering within range 250-450℃, due to temper brittleness.
Caution: heating temperatures, heating rates, soaking time will vary according on different factors, like piece size, piece shape, furnace type, quenching medium, transfer facilities.
MIM 4340 Post Processing
Machining
Whether hardened or tempered, steel 4340 is still regarded as readily machinable, the common machining operations includes: sawing, turning, drilling.
Welding
4340 welding in the hardened and tempered condition is not recommended, this should be avoided if possible. It is preferred to weld in annealed condition, cool the work-piece immediately to hand warm, then stress relieving at 640-660℃.
Conclusion
ZCMIM has more than 15 year experience in MIM 4340 technology. We apply different alloy power size, sintering temperatures, heat treatment to achieve specific density and mechanical properties. Contact us for your next MIM 4340 project.







