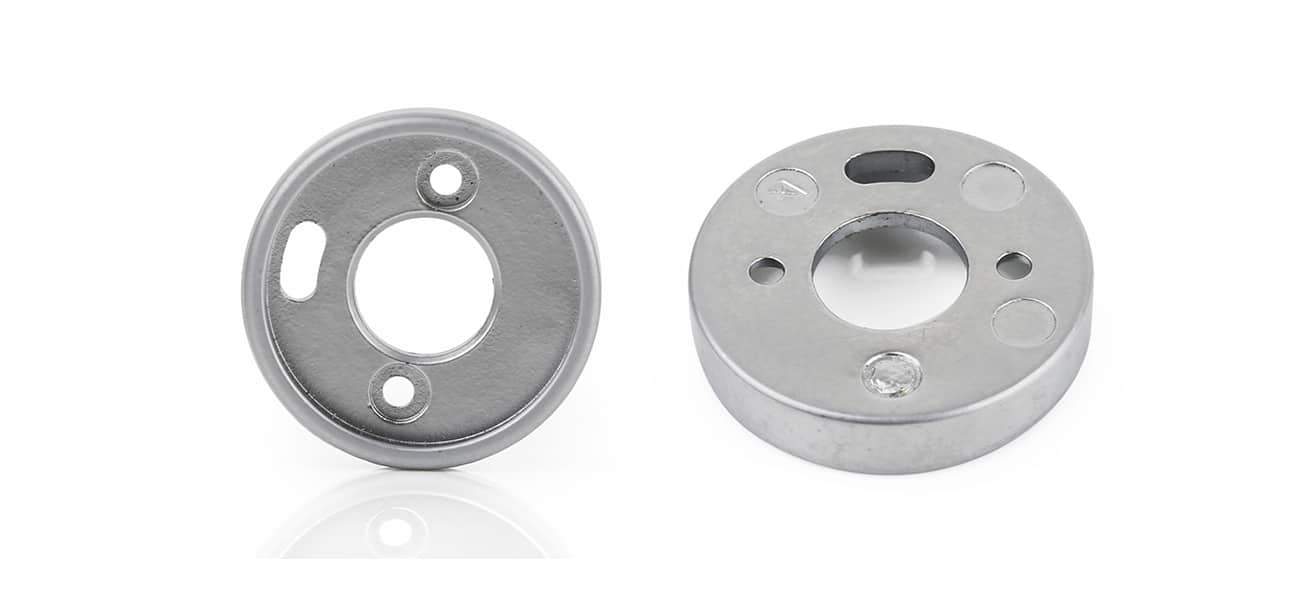
MIM 304
MIM 304 Introduction
MIM 304 is another austenitic grade stainless steel, it has high-temperature resistance, oxidation resistance and corrosion resistance.
It is commonly known as A2 stainless steel, or 18/8 stainless stee in cookware industry, UNS S30400 in numbering system, SUS304 in Japanese equivalent grade, 1.4301 in European norm. MIM 304 has good stability below 540℃, it is the best choice for components without machining operations.
Both stainless steel 304 and 316L are suitable for normal pressing and sintering in metal injection molding (MIM). However, stainless steel 316L has the highest degree of corrosion resistance, normally in application of paint additives and chemical filtration.
MIM 304L & 304H
Chemical Composition
The common composition of MIM 304 after sintering is as following:
| Stainless steel 304 | Iron | Nickel | Silicon | Carbon | Chromium | Phosphorus | Manganese | Nitrogen | Sulfur |
| Percent by Weight | BaL. | 8.00-10.50 | 0.75 | 0.08 | 18.00-20.00 | 0.045 | 2.00 | 0.10 | 0.030 |
Carbon Content
As stainless steel 304 are divided into different types by carbon content levels: 304L, 304 and 304L. The different carbon content is <0.03%, >0.03%, >0.05% respectively. All these classifications have the same nominal chromium and nickel content, and provide the same corrosion resistance, ease of fabrication and weldability.
In MIM industry, the most common 304 materials are MIM 304L and MIM 304H. Although MIM 304L and 304H have uniform performance in most corrosive environments, there are still some unique properties and applications.
MIM 304L
The carbon content of MIM 304L is restricted at maximum of 0.03%, this can prevent sensitization during welding process, and finally prevent inter-granular corrosion. MIM 304L can be applied for corrosive applications with further welding process, such as tanks and pipes.
Sensitization is the formation of chromium carbides along grain boundaries, once expose stainless steel to temperatures in the range of 480-820℃. The formation of chromium carbide will reduce corrosion resistance along the grain boundaries. Therefore, stainless steel 304 is susceptible to unanticipated corrosion by this inter-granular corrosion
| Material | Proof Stress | Tensile Strength | Elongation(% in 25.4mm) | Hardness Max | |
| HB | HRB | ||||
| Stainless steel 304L | 170Mpa | 485Mpa | 40% | 201 | 92 |
ZCMIM engineering team can apply different MIM 304L feedstock for different application requirement. Please check the chemical composition and property parameters of different SS304 feedstocks in the following files.
MIM 304H
MIM 304H has carbon content of maximum 0.08 %, which provides optimal high temperature strength. Therefore, it is applied for structural and pressure-containing applications above 500℃ and up to 800℃. It has good oxidation resistance in intermittent service to 870℃ and in continuous service to 920℃. MIM 304H also becomes sensitized in welding at the temperature of 425-860℃, this will reduce aqueous corrosion resistance.
As in extreme thermal testing, MIM 304H still has good physical durability. It is suitable for a wide scope of industrial applications, even in severe processing and storage environments, like boilers and pressure vessels. There is no doubt that 304H stainless steel has superb creep strength in both short and long term applications.
| Material | Proof Stress | Tensile Strength | Elongation(% in 25.4mm) | Hardness Max | |
| HB | HRB | ||||
| Stainless steel 304H | 205Mpa | 515Mpa | 40% | 201 | 92 |
Please check the chemical composition and property parameters in the following file.
Properties Comparison
MIM 304L has lower carbon content than MIM 304H, this minimizes or eliminates carbide precipitation (sensitization) during the welding process. Therefore, MIM 304L can be applied in the ‘as-welded’ state after MIM sintering, even in severely corrosive environments. We can notice that it will degrade faster at the weld joints in all MIM 304 applications. At times, MIM 304L has a lower corrosion rate than MIM 304H. Once require stronger corrosion resistance, MIM 316L is the optimal stainless steel option.
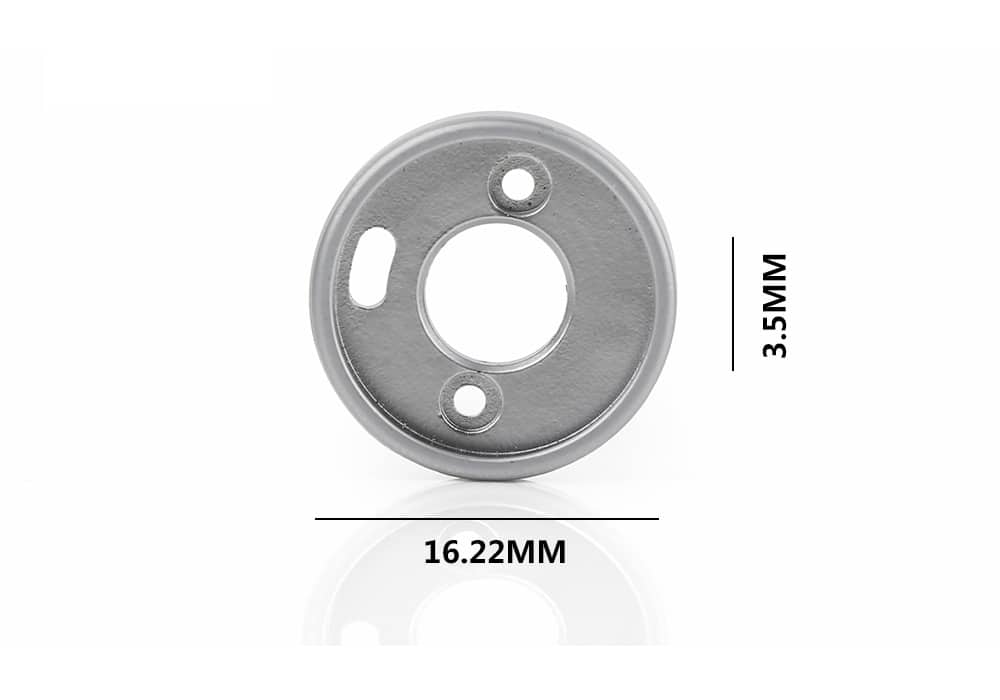

Typical Mechanical Properties
| Material | Density | Tensile Strength | Yield Strength(0.2%) | Hardness | Elongation(% in 25.4mm) |
| Stainless steel 304 | ≥7.75g/cm³ | ≥480Mpa | ≥160Mpa | 100-150 HV10 | ≥40% |
Stainless steel 304 is one of the most common austenitic stainless steel in metal injection molding industry. It contains high nickel content between 8 and 10.5 % by weight, high chromium at 18 to 20 % by weight. Other alloy elements including: manganese, silicon, and carbon.
The high amounts of chromium and nickel in MIM 304 provide excellent corrosion resistance, the common application of 304 stainless steel including:
- Electronic appliances: refrigerators and dishwashers
- Commercial food process equipment
- Fasteners, piping, heat exchangers
- Structural components in corrosion environment
As an austenitic stainless steel, MIM 304 has less electrically and thermally conductive than carbon steel. It is also magnetic, but less magnetic than steel. MIM 304 has higher corrosion resistance than regular steel, and easy formation into various shapes.
Specific Properties
MIM 304 has excellent resistance in a wide range of atmospheric environments and corrosive media.
Normally in warm chloride environments, MIM 304 is subject to pitting and crevice corrosion, and stress corrosion cracking above 60℃.
MIM 304 is also very sensitive to thiosulfate anions at room temperature. Once contact with pyrite or sulfide materials, it will undergo severe pitting corrosion problems.
In more severe corrosion conditions, such as chlorides or acidic applications. MIM 316L will replace 304 to be the preferred alloy.
MIM 304 Applications
MIM 304 is used for various household and industrial application such as:
- Food handling and processing equipment
- Machinery components
- Utensils and exhaust manifolds
- Exterior accents in architectural field
Major Difference between 304 and 316L
Different Corrosion Resistance Level
Comparing MIM 316L, there is a major difference in chemical composition between 304 and 316L stainless steel. MIM 316L contains a significant amount of molybdenum with 2-3% in weight. While only trace amount in MIM 304. This higher molybdenum content results in higher corrosion resistance of MIM 316L.
MIM 316L is the most suitable choice in anustentic stainless steel for marine applications. Such as: chemical processing and storage equipment, refinery equipment, medical devices, marine environments with chlorides presentation.
Application Situation
MIM 304 is the better choice than MIM 316L in the following situations:
- Applications require excellent formability. The high molybdenum content in MIM 316L have adverse effects on formability in manufacturing process.
- Applications with cost concerns. MIM 304 is more affordable than MIM 316L.
MIM 316L is more suitable than MIM 304 in following applications:
- Environments with amount of corrosive elements.
- Applications are underwater or exposed to water consistently.
- Requirements with greater strength and hardness.
Conclusion
Stainless steel 304 provides excellent combination of high-temperature resistance, oxidation resistance and corrosion resistance. It is a cost-effective material for various stainless steel applications.